An interesting application of the Pythagorean doctrine of geometric solids as expounded by Plato is found in The Canon. “Nearly all the old philosophers,” says its anonymous author, “devised an harmonic theory with respect to the universe, and the practice continued till the old mode of philosophizing died out. Kepler (1596), in order to demonstrate the Platonic doctrine, that the universe was formed of the five regular solids, proposed the following rule. ‘The earth is a circle, the measurer of all. Round it describe a dodecahedron; the circle inclosing this will be Mars. Round Mars describe a tetrahedron; the sphere inclosing this will be Jupiter. Describe a cube round Jupiter; the sphere containing this will be Saturn. Now inscribe in the earth an icosahedron; the circle inscribed in it will be Venus. Inscribe an octahedron in Venus; the circle inscribed in it will be Mercury’ (Mysterium Cosmographicum, 1596). This rule cannot be taken seriously as a real statement of the proportions of the cosmos, fox it bears no real resemblance to the ratios published by Copernicus in the beginning of the sixteenth century. Yet Kepler was very proud of his formula, and said he valued it more than the Electorate of Saxony. It was also approved by those two eminent authorities, Tycho and Galileo, who evidently understood it. Kepler himself never gives the least hint of how his precious rule is to be interpreted.” Platonic astronomy was not concerned with the material constitution or arrangement of the heavenly bodies, but considered the stars and planers primarily as focal points of Divine intelligence. Physical astronomy was regarded as the science of “shadows,” philosophical astronomy the science of “realities.”
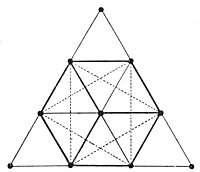
THE TETRACTYS. Theon of Smyrna declares that the ten dots, or tetractys of Pythagoras, was a symbol of the greatest importance, for to the discerning mind it revealed the mystery of universal nature. The Pythagoreans bound themselves by the following oath: “By Him who gave to our soul the tetractys, which hath the fountain and root of ever-springing nature.”
THE CUBE AND THE STAR. By connecting the ten dots of the tetractys, nine triangles are formed. Six of these are involved in the forming of the cube. The same triangles, when lines are properly drawn between them, also reveal the six-pointed star with a dot in the center. Only seven dots are used in forming the cube and the star. Qabbalistically, the three unused corner dots represent the threefold, invisible causal nature of the universe, while the seven dots involved in the cube and the star are the Elohim–the Spirits of the seven creative periods. The Sabbath, or seventh day, is the central dot.
Next: Pythagorean Mathematics
Index

Moe is the founder of GnosticWarrior.com. He is a father, husband, author, martial arts black belt, and an expert in Gnosticism, the occult, and esotericism.