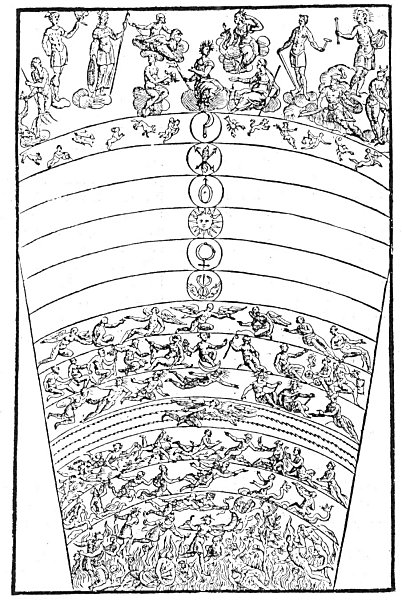
2. The architect Ctesiphon, in the fifth century B.C., submitted to the Ionian cities a plan for erecting a joint monument to their patron goddess, Diana. The place chosen was Ephesus, a city south of Smyrna. The building was constructed of marble. The roof was supported by 127 columns, each 60 feet high and weighing over 150 tons. The temple was destroyed by black magic about 356 B.C., but the world fixes the odious crime upon the tool by means of which the destruction was accomplished–a mentally deranged man named Herostratus. It was later rebuilt, but the symbolism was lost. The original temple, designed as a miniature of the universe, was dedicated to the moon, the occult symbol of generation.
3. Upon his exile from Athens, Phidias–the greatest of all the Greek sculptors–went to Olympia in the province of Elis and there designed his colossal statue of Zeus, chief of the gods of Greece. There is not even an accurate description of this masterpiece now in existence; only a few old coins give an inadequate idea of its general appearance. The body of the god was overlaid with ivory and the robes were of beaten gold. In one hand he is supposed to have held a globe supporting a figure of the Goddess of Victory, in the other a scepter surmounted by an eagle. The head of Zeus was archaic, heavily bearded, and crowned with an olive wreath. The statue was seated upon an elaborately decorated throne. As its name implies, the monument was dedicated to the spirit of the planet Jupiter,–one of the seven Logi who bow before the Lord of the Sun.
4. Eliphas Levi includes the Temple of Solomon among the Seven Wonders of the World, giving it the place occupied by the Pharos, or Lighthouse, of Alexandria. The Pharos, named for the island upon which it stood, was designed and constructed by Sostratus of Cnidus during the reign of Ptolemy (283-247 B.C.). It is described as being of white marble and over 600 feet high. Even in that ancient day it cost nearly a million dollars. Fires were lighted in the top of it and could be seen for miles out at sea. It was destroyed by an earthquake in the thirteenth century, but remains of it were visible until A.D. 1350. Being the tallest of all the Wonders, it: was naturally assigned to Saturn, the Father of the gods and the true illuminator of all humanity.
5. The Mausoleum at Halicarnassus was a magnificent monument erected by Queen Artemisia in memory of her dead husband, King Mausolus, from whose name the word mausoleum is derived. The designers of the building were Satyrus and Pythis, and four great sculptors were employed to ornament the edifice. The building, which was 114 feet long and 92 feet wide, was divided into five major sections (the senses) and surmounted by a pyramid (the spiritual nature of man). The pyramid rose in 24 steps (a sacred number), and upon the apex was a statue of King Mausolus in a chariot. His figure was 9 feet 9½ inches tall. Many attempts have been made to reconstruct the monument, which. was destroyed by an earthquake, but none has been altogether successful. This monument was sacred to the planet Mars and was built by an initiate for the enlightenment of the world.
6. The Gardens of Semiramis at Babylon–more commonly known as the Hanging Gardens–stood within the palace grounds of Nebuchadnezzar, near the Euphrates River. They rose in a terrace-like pyramid and on the top was a reservoir for the watering of the gardens. They were built about 600 B.C., but the name of the landscape artist has not been preserved. They symbolized the planes of the invisible world, and were consecrated to Venus as the goddess of love and beauty.
7. The Great Pyramid was supreme among the temples of the Mysteries. In order to be true to its astronomical symbolism, it must have been constructed about 70,000 years ago. It was the tomb of Osiris, and was believed to have been built by the gods themselves, and the architect may have been the immortal Hermes. It is the monument of Mercury, the messenger of the gods, and the universal symbol of wisdom and letters.
TROPHONIUS OF LEBADIA.
from Historia Deorum Fatidicorum. Trophonius and his brother Agamedes were famous architects. While building a certain treasure vault, they contrived to leave one stone movable so that they might secretly enter and steal the valuables stored there. A trap was set by the owner, who had discovered the plot, and Agamedes was caught. To prevent discovery, Trophonius decapitated his brother and fled, hotly pursued. He hid in the grove of Lebadia, where the earth opened and swallowed him up. The spirit of Trophonius thereafter delivered oracles in the grove and its caverns. The name Trophonius means “to be agitated, excited, or roiled.” It was declared that the terrible experiences through which consultants passed in the oracular caverns so affected them that they never smiled again. The bees which accompany the figure of Trophonius were sacred because they led the first envoys from Bœtia to the site of the oracle. The figure above is said to be a production of a statue of Trophonius which was placed on the brow of the hill above the oracle and surrounded with sharply pointed stakes that it could not be touched.

Moe is the founder of GnosticWarrior.com. He is a father, husband, author, martial arts black belt, and an expert in Gnosticism, the occult, and esotericism.