Several ancient authors, including Macrobius, have affirmed that Serapis was a name for the Sun, because his image so often had a halo of light about its head. In his Oration Upon the Sovereign Sun, Julian speaks of the deity in these words: “One Jove, one Pluto, one Sun is Serapis.” In Hebrew, Serapis is Saraph, meaning “to blaze out” or “to blaze up.” For this reason the Jews designated one of their hierarchies of spiritual beings, Seraphim.
The most common theory, however, regarding the origin of the name Serapis is that which traces its derivation from the compound Osiris-Apis. At one time the Egyptians believed that the dead were absorbed into the nature of Osiris, the god of the dead. While marked similarity exists between Osiris-Apis and Serapis, the theory advanced by Egyptologists that Serapis is merely a name given to the dead Apis, or sacred bull of Egypt, is untenable in view of the transcendent wisdom possessed by the Egyptian priestcraft, who, in all probability, used the god to symbolize the soul of the world (anima mundi). The material body of Nature was called Apis; the soul which escaped from the body at death but was enmeshed with the form during physical life was designated Serapis.
C. W. King believes Serapis to be a deity of Brahmanic extraction, his name being the Grecianized form of Ser-adah or Sri-pa, two titles ascribed to Yama, the Hindu god of death. This appears reasonable, especially since there is a legend to the effect that Serapis, in the form of a bull, was driven by Bacchus from India to Egypt. The priority of the Hindu Mysteries would further substantiate such a theory.
Among other meanings suggested for the word Serapisare: “The Sacred Bull,” “The Sun in Taurus,” “The Soul of Osiris,” “The Sacred Serpent,” and “The Retiring of the Bull.” The last appellation has reference to the ceremony of drowning the sacred Apis in the waters of the Nile every twenty-five years.
THE LION-FACED LIGHT-POWER.
From Montfaucon’s Antiquities. This Gnostic gem represents by its serpentine body the pathway of the Sun and by its lion head the exaltation of the solar in the constellation of Leo.
A SYMBOLIC LABYRINTH.
From Montfaucon’s Antiquities. Labyrinths and mazes were favored places of initiation among many ancient cults. Remains of these mystic mazes have been found among the American Indians, Hindus, Persians, Egyptians, and Greeks. Some of these mazes are merely involved pathways lined with stones; others are literally miles of gloomy caverns under temples or hollowed from the sides of mountains. The famous labyrinth of Crete, in which roamed the bull-headed Minotaur, was unquestionably a place of initiation into the Cretan Mysteries.
p. 27
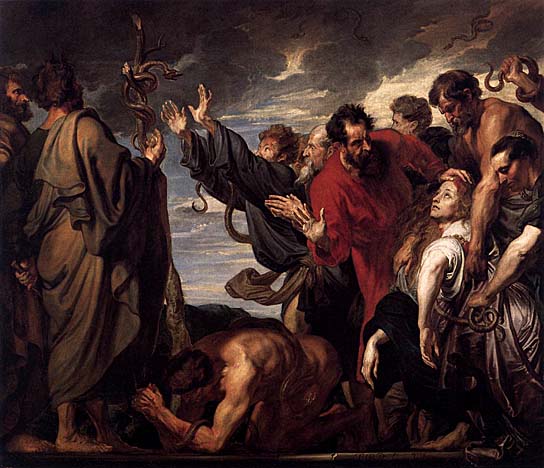
There is considerable evidence that the famous statue of Serapis in the Serapeum at Alexandria was originally worshiped under another name at Sinope, from which it was brought to Alexandria. There is also a legend which tells that Serapis was a very early king of the Egyptians, to whom they owed the foundation of their philosophical and scientific power. After his death this king was elevated to the estate of a god. Phylarchus declared that the word Serapis means “the power that disposed the universe into its present beautiful order.”
In his Isis and Osiris, Plutarch gives the following account of the origin of the magnificent statue of Serapis which stood in the Serapeum at Alexandria:
While he was Pharaoh of Egypt, Ptolemy Soter had a strange dream in which he beheld a tremendous statue, which came to life and ordered the Pharaoh to bring it to Alexandria with all possible speed. Ptolemy Soter, not knowing the whereabouts of the statue, was sorely perplexed as to how he could discover it. While the Pharaoh was relating his dream, a great traveler by the name of Sosibius, coming forward, declared that he had seen such an image at Sinope. The Pharaoh immediately dispatched Soteles and Dionysius to negotiate for the removal of the figure to Alexandria. Three years elapsed before the image was finally obtained, the representatives of the Pharaoh finally stealing it and concealing the theft by spreading a story that the statue had come to life and, walking down the street leading from its temple, had boarded the ship prepared for its transportation to Alexandria. Upon its arrival in Egypt, the figure was brought into the presence of two Egyptian Initiates–the Eumolpid Timotheus and Manetho the Sebennite–who, immediately pronounced it to be Serapis. The priests then declared that it was equipollent to Pluto. This was a masterly stroke, for in Serapis the Greeks and Egyptians found a deity in common and thus religious unity was consummated between the two nations.

Moe is the founder of GnosticWarrior.com. He is a father, husband, author, martial arts black belt, and an expert in Gnosticism, the occult, and esotericism.